Syntax of a Programming Language
The Syntax of a Programming Language is the set of rules that defined in that programming language in order to express how the combinations of symbols are formed.
Syntax is differed into two main categories.
- Abstract Syntax --> Provide definition for the constructs
- Concrete Syntax --> Provide definitions of the form of the constructs
E.g. In Java while loop is defined as
While(booleanValue){//Statements goes here}
Semantics of a Programming Language
Semantics reveals the meaning of a syntactically correct programming language in expressions, statements, program units. Semantics of a programming language also can be divided into two different categories.
Static Semantics
For compiled languages static semantics are usually tested at the compile time.
E.g. checking that every identifier is declared before it is used (in languages that require such declarations)
Dynamic Semantics
As the above classification there are three types of Dynamic Semantics. Dynamic Semantics are usually tested while at the runtime. Dynamic Semantics of a Programming language defines how and when the various constructs of a language should produce a program behavior.
e.g In java
e.g In java
if(a==b){return;}
Meaning of this statement is derived by executing this program on a computer. (This is what we called operational semantics also in the same category of Dynamic semantics)
Ambiguity of a Programming Language
If a statement constructed by using a particular grammar has more than one parse tree; it is said to be that grammar is ambiguous.
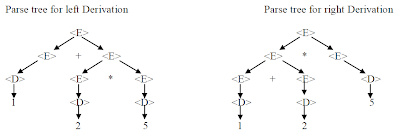
E.g. Simple example
<E> --> <D>
<E> --> <E>
<E> --> <E> + <E> |<E> - <E> |<E> * <E> |<E> / <E>
<D> --> 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9
Let’s consider statement 1+2*5 for the above grammar
Above grammar is ambiguous since it has two parse trees and the left derivation tree give the answer 11 which is correct and the right derivation tree gives 15 which is incorrect.












No comments:
Post a Comment